Abstract
Introduction: BMT CTN 0201, a randomized clinical trial, demonstrated that overall survival is equivalent between recipients of allogeneic bone marrow (BM) vs. granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) mobilized peripheral blood grafts. Increased graft failure was observed in recipients of BM grafts, while recipients of G-CSF mobilized peripheral blood (G-PB) grafts had more chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) (Anasetti NEJM 2012). Donor plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) content is associated with increased overall survival and decreased acute GvHD related mortality among recipients of BM grafts from unrelated donors, but not G-PB grafts (Waller JCO 2014). We have previously shown that in murine bone marrow transplant (BMT), donor pDC from the bone marrow reduce GvHD and improve survival while maintaining graft-versus-leukemia effect when added to grafts containing purified hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) and T cells (Lu BLOOD 2012). We hypothesized that the difference in chronic GvHD observed in BMT CTN 0201 is due to donor pDC content and function that vary according to graft source differences: BM vs. G-PB.
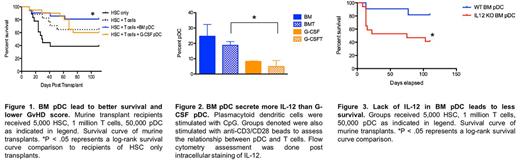
Methods and Results: To assess the effects of pDC source on overall survival and GvHD, we used an established MHC mismatched model of murine BMT (C57BL/6 to B10.BR). To test whether the graft source of donor pDC was relevant to GvHD, we used flow cytometry to sort populations of HSC and T cells from untreated donor mice and pDC from either untreated BM or G-CSF mobilized splenocytes. We performed a BMT with 5,000 HSC, 1 million T cells, and either 50,000 BM or G-PB pDC from C57BL/6 mice into B10.BR recipients. Overall survival was significantly reduced among recipients of G-PB donor pDC compared with recipients of BM pDC, while late stage GvHD was higher in recipients of G-PB pDC (Fig. 1).
To determine possible differences in function of pDC from each graft source: BM vs. G-PB, we assessed cytokine and enzymatic profiles by flow cytometry. Intracellular levels of IL-12 was significantly higher in CpG stimulate purified BM pDC compared to G-PB pDC co-cultured with purified T cells stimulated by anti-CD3/CD28 beads (Fig. 2). Additionally, Th1 polarization was higher in T cells sitmulated with anti-CD3/CD38 and cocultured with BM pDC, resulting in higher TNFa and IFNy production from these T cells. Levels of intracellular cytokines IFNa and IL-10 and levels of IDO showed no significant differences between pDC from Bm vs. G-PB.
The transplant detailed above was repeated with BM pDC from wild-type (WT) mice or IL-12 KO mice. Overall survival of recipients of IL-12 KO BM pDC was significantly reduced when compared with recipients of WT BM pDC (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: These data confirm that donor BM pDC are protective against lethal GvHD and indicate a loss of GvHD protection in donor pDC from G-PB grafts due to decreased inducible IL-12 synthesis. Because both graft sources are widely used clinically, mechanisms to recapitulate the immune-modulating properties of BM pDC in pDC of G-PB grafts are of great interest to the BMT field.
Waller: National Institutes of Health: Research Funding; Celldex: Consultancy; Cerus: Equity Ownership; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Katz Foundation: Research Funding; AMGEN: Consultancy; Chimerix: Equity Ownership; Helocyte: Consultancy; Cambium Medical Technologies: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties; PRA: Consultancy; Coulter Foundation: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal